Why SaaS is becoming the Go-to service?
What is SaaS?
A Software as a Service solution lets users to access and use software applications online, without having to install the application on their own computer. The service provider hosts the software for its customers and provides them with an interface that enables them to log in and make changes or create fresh content within the system. SaaS stands for 'Software as a Service.
Types of SaaS :
There are three key types of SaaS solutions available today:
Cloud based -
A cloud based SAAS solution means you have your data stored away from where it's used by the app itself.
On premise -
An on premises SAAS solution requires all of the components needed to run the business to live onsite at one location.
Hybrid -
A hybrid SAAS solution combines both on site and off site capabilities.
Horizontal vs Vertical SaaS
Horizontal SaaS
Horizontal SaaS refers to any web-hosted product which serves a lot of clients simultaneously. Horizontally scalable products allow companies to grow easily because each client only pays for resources consumed; no additional hardware investment needed.
Vertical SaaS
If you're looking for something simple then upright scaling might work best for you. Vertical SaaS focuses on providing a single function and letting businesses to scale up or down according to demand. For instance, a company could start small with just 10 employees using a basic version of the solution before expanding into larger offices once they've proven themselves.
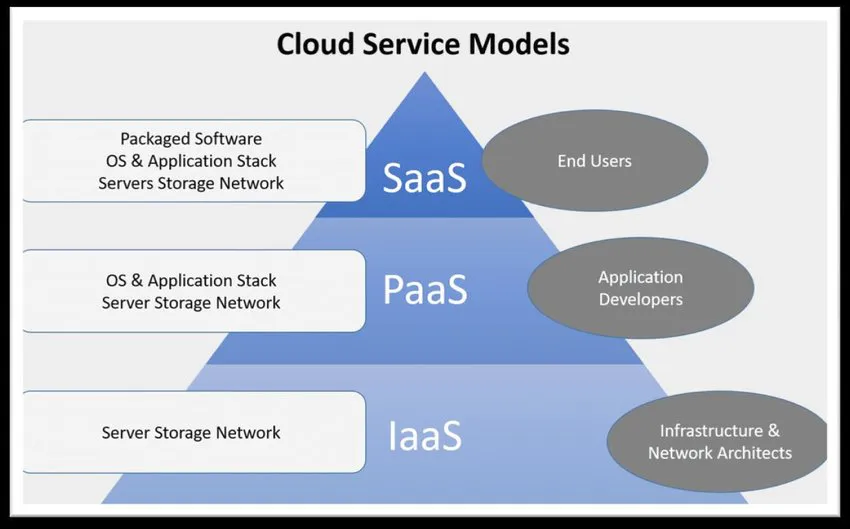
SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS
SaaS stands for 'Software as a Service'. These days, we often hear about "IaaS" and "PaaS". But what does this mean exactly? SaaS is simply a way to provide software functionality through the internet instead of installing the software onto our computers ourselves.
IaaS stands for 'Infrastructure As a Service'. With IaaS, you get access to computing power plus storage capacity. If you were to build a website yourself, you would need to buy a server, hire someone to set it up and connect it to the Internet, and then purchase hard drive space. That sounds like a lot of effort! By comparison, with Iaas, you don't actually do anything except sign up for the service. Your IT team handles everything else.
PaaS stands for 'Platform As a Service'. The main difference between PaaS and IaaS is that in order to make an application available via PaaS, you must already own the programming language and tools necessary to create applications. When you choose PaaS, you essentially rent the underlying infrastructure so that you can focus solely on creating the actual apps.
How does software as a service work?
Software as a service is a way of delivering software functionality via internet connections instead of installing the software onto individual computers on a subscription model either monthly, yearly or lifetime deal basis. With SaaS, the user signs up for a subscription plan and gets access to the full range of features offered by the software. Users do not need to download, install, configure or maintain the software. Instead, the vendor takes care of all of that. Some key differences between SaaS and traditional desktop software include:
- No installation/upgrade necessary
- Users don't need to purchase licenses or upgrade versions
- Vendor manages updates & maintenance
- Costs are typically lower than purchasing software outright
- Handles Data storage centrally
- Ease of Use
With SaaS, software vendors provide easy ways for end users to sign up, login, view usage statistics, manage settings, etc. The software runs in the background without needing frank interaction from the customer. Most applications offer an online dashboard so customers can monitor their own progress, make changes, add new team members, etc.
Why you should buy SaaS?
There's no doubt that there are many benefits to choosing Software-As-A-Service over other options such as buying your own computer hardware or hiring people to use them.
Pros:
- Flexibility - You have complete control over how much time you spend managing your data center versus focusing on growing your business.
- Lower costs - Since you aren't paying for physical equipment, you won't be spending money on electricity bills, repairs, upgrades, or depreciation.
- Security - Data centers are more secure because home office locations are far from where hackers could potentially gain entry. Also, since you never touch any explicit servers at your location, you'll always know who has access to which information.
- Reduced risk - There will be less chance of losing precious data if something happens to your local network.
- Simplicity - It's easier to scale when using cloud based services rather than setting up your own environment.
Cons:
- Limited flexibility - While some companies may find this limitation okay, others might want more customization capabilities. For example, if you wanted to run multiple instances of a special program simultaneously, you'd have to pay extra for additional virtual machines. This means that you wouldn't be able to take advantage of economies of scale.
- Lack of security - Because most providers let third party developers to write code into their systems, you don't really know what kind of malicious code these external parties might be putting into your system. If you were running it yourself, you would have total control over everything.
- Less reliability - When you outsource certain aspects of IT management to someone else, you lose control over things like backups, scalability, uptime, etc.
- More expensive - Depending on the provider, prices vary widely. But, even though the cost per hour varies greatly, the overall price tag usually ends up being prime anticipated to the fact that you're paying for infrastructure upfront.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to accessing resources through web portals. These resources may include things like email accounts, file sharing networks, databases, websites, virtual machines, desktops, portable devices, etc. A good example of this type of technology is Gmail.com. This site lets its users to store emails, share files, chat, play games, etc., but it also provides these functions remotely. Users only need to log onto the website and start working. They don't need to install anything locally.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
The basic idea behind cloud computing is pretty simple. Instead of having one large server with all the programs installed, each user gets his/her own personal copy of those same programs. Each person uses whatever he wants whenever he needs it. All the software resides in detached computers called "servers" instead of on individual PCs. This makes it possible to use just about any device as long as there is an internet connection available.
Features of Cloud Computing:
There are several different types of clouds. The two main ones are private clouds and public clouds. Private Clouds consist of dedicated hardware owned by a single company or organization while Public Clouds share among many organizations. Here are some other characteristics of both types of clouds:
- Private Clouds
Dedicated Hardware – You can configure your own computer architecture within a private cloud. Your configuration may differ depending upon how much power you require.
Some examples of common configurations are:
1 CPU, 2 CPUs, 4 CPUs, 8 CPUs, 16 CPUs, 32 CPUs, and 64 CPUs
- Public Clouds
Shared Resources – There's no limit to the number of people who can access the services provided via a public cloud. It could potentially house hundreds of thousands of servers.
Examples of popular public clouds include:
Amazon Web Services, Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure, Rackspace Hosting, Softlayer, and VMware vSphere.
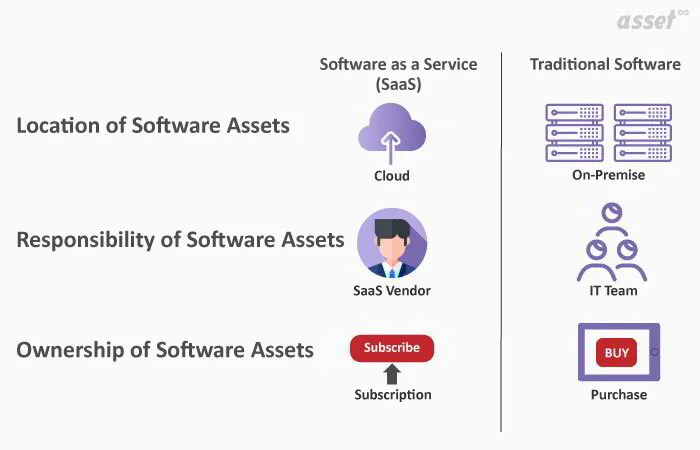
SaaS Vs. Traditional Software Solutions
A SaaS solution works differently than traditional software solutions. In a traditional environment, when a customer buys a piece of software they get a physical disk containing the program itself. Customers then must install the program themselves before using it. With a SaaS application, customers simply download the app from the Internet and begin using it at once.
Challenges & Risks Of SaaS Applications
One major challenge associated with SaaS applications is security: Because the data stored on the client side is not under control of the vendor, they have little incentive to keep their clients' information secure. If hackers gain access to someone else’s data, they will be able to do so regardless if the data was hosted on-premises or offsite.
Another risk that comes along with SaaS apps is privacy: Since most SaaS vendors offer free versions for testing purposes, they often collect lots of sensitive data without asking permission first. As such, companies should always make sure they know what kind of data they're collecting and whether they'll be storing it permanently or temporarily.
Risk of Losing Critical Business Functionality Due To Unexpected Downtime: When working with SaaS applications, businesses need to understand that these systems aren't infallible. They might experience unplanned outages at times which means that users won't be able to perform certain functions until everything has been fixed. For example, if a business relies heavily on its email system, unexpected downtime would mean losing important emails and documents forever.
Security Concerns Associated With Using Free Trial Versions
When choosing between a paid version and a trial version, consider the following factors:
Cost - A free trial usually costs less money than purchasing a product outright. However, this doesn't necessarily translate into better value because the quality of service offered during the trial period isn't guaranteed.
Risk - The cost of an first purchase does come down after the trial period ends but there's still a chance that the user will decide against buying the full package later in time. This is especially true when considering enterprise products where support contracts typically cover only one year. After that point, the company loses all rights to use the software unless the license expires.
Time - When deciding between paying upfront versus waiting until after the trial period is over, think about how long you want to wait. Will your organization feel comfortable continuing to pay monthly fees even though some functionality may not work? Consider signing up for a 30 day free trial instead. It gives you enough time to test the product thoroughly while also giving you plenty of opportunity to cancel right away if things don't go as planned.
Also, many SaaS providers provide "free" trials with limitations. Some charge per user/per month; others limit usage to distinct features (e.g., number of pages viewed ). In either case, it pays to read through the terms carefully before agreeing to any contract.
Some Examples of Companies that offer SaaS
> Google Workspace
Pricing starts at $5/user/month.
Pros: Unlimited storage space, unlimited domains, easy set-up process.
Cons: No desktop application, can't install locally.
> Microsoft Office 365
Pricing starts around $6-$8/user/month depending on subscription type.
Pros: Great feature list including collaboration tools, online document editing, eDiscovery, etc.
Cons: Requires Microsoft Windows OS, requires annual maintenance fee, limits customizations.
> Salesforce CRM
Pricing starts from $9/user/month.
Pros: Easy setup process, no hardware requirements, mobile app available
Cons: Bounded customization options, limited API capabilities.
> Zoho Creator
Pricing starts under $10/user/month.
Pros: Can create websites using drag & drop interface, offers templates, provides SEO services.
Cons: Doesn’t offer much beyond basic website creation.
> Adobe Creative Cloud
Pricing starts below $20/user/month.
Pros: Offers extensive library of design elements, video production tools, web development tools, photo editing tools, etc.
Cons: Not suitable for small businesses due to high price tag.
> Microsoft SharePoint Online
Pricing starts below $15/user/month. Includes 1TB cloud drive.
Pros: Lets users to collaborate and share documents across multiple devices.
Cons: Only supports MS Word 2007 or newer versions.
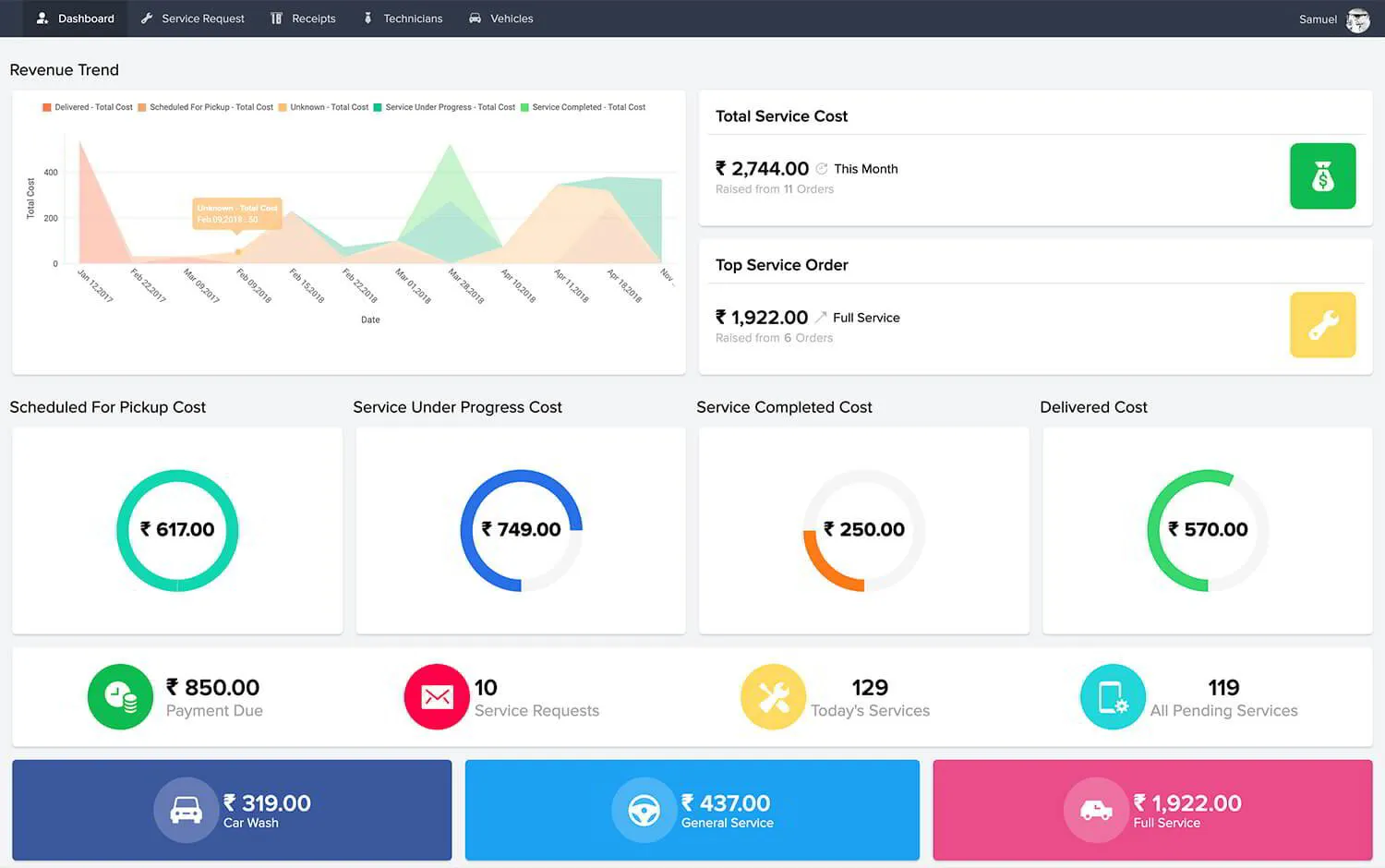
Don't know which application is the best for you or your business? Want to find the best software before using Cloud?
Try our calculator which uses your inputs based on your need/preferences to deliver the best application for you to use.
To sum up,
As we've seen throughout this article, cloud computing can save organizations sizable amounts of money by reducing IT infrastructure expenses. But just like other types of technology, using cloud services requires careful consideration regarding potential risks and drawbacks. By taking advantage of the benefits provided by cloud solutions, businesses can enjoy more efficient operations and increased productivity.
I'd say that most people would agree that the biggest benefit of cloud based applications are speed and convenience. They're able to access their data anywhere they have internet connection which means anytime, anywhere. I'm sure you could find someone who says otherwise, but those arguments aren't very convincing. If anything, the biggest drawback of these apps seems to be security. The fact that all information is stored in one place makes it easier for hackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive company files.
What are your views about SaaS? Is it good for in the long run as well? Is this the way to save your money or to make you spend more money? Will investing in SaaS result in a profit?
Hope this helped!
Like What You're Reading?
Sign up for more articles on our website!
Related Articles
Best Email Marketing software for 2021
How AppSumo Does Black Friday?
Best Quiz builder tools of 2021
F.A.Q'S
What is SaaS?
In more detailed lines, SaaS is a method of remotely delivering software, meaning that the service contractor can access it from any device with an Internet connection.
In this web-based software model, vendors host and maintain the servers, databases, and code that make up the application.
What is the difference between SaaS and cloud computing?
Cloud is a collection of computers, servers, and databases that are connected together in a way that users can grant access to share their use.
All cloud programs are run by underlying software, SaaS specifically refers to commercial software applications that are delivered via the cloud.
Who owns my data?
To start a contract on a platform, data and information from the contractor is required.
Some people are reluctant because someone might access their data, also that the software company will “own” such private information. You should pay attention to this when negotiating a service level agreement (SLA) with your SaaS provider.
Is my data secure?
Security is a priority when it comes to allowing someone else to keep data critical to your business, especially for large companies.
The good news is that SaaS vendors are actually able to invest a lot more in security, backups and maintenance than any small to medium business.
What if my SaaS provider goes out of business?
SaaS is a business, and any business is subject to failure or termination.
The data, however, remains yours. Most SaaS providers prepay their data center hosting company to “keep the lights on” for a while.
This prepaid fee aims to protect companies to ensure their data is accessible in case something happens to the vendor.